Agricultural Machinery Training in Germany: How This Field Is Typically Structured
Agricultural machinery training in Germany is often described as a blend of technical foundations and supervised, real-world practice around modern farm equipment. This article explains how the field is typically structured: common learning blocks (mechanics, hydraulics, basic electrics, diagnostics), workshop routines, and the role of safety standards and operating procedures when working with machinery. It also outlines how training environments may be organized—classroom + lab + hands-on sessions—and what to compare across options, such as duration, prerequisites, assessments, and the kinds of equipment used, without promising specific outcomes.

Agricultural machinery has become increasingly sophisticated, requiring skilled operators and technicians who understand both the mechanical principles and the practical application of modern farm equipment. In Germany, training programs in this field are designed to equip participants with the knowledge and hands-on experience needed to work safely and effectively with a wide range of machinery.
How Is Agricultural Machinery Training Typically Structured
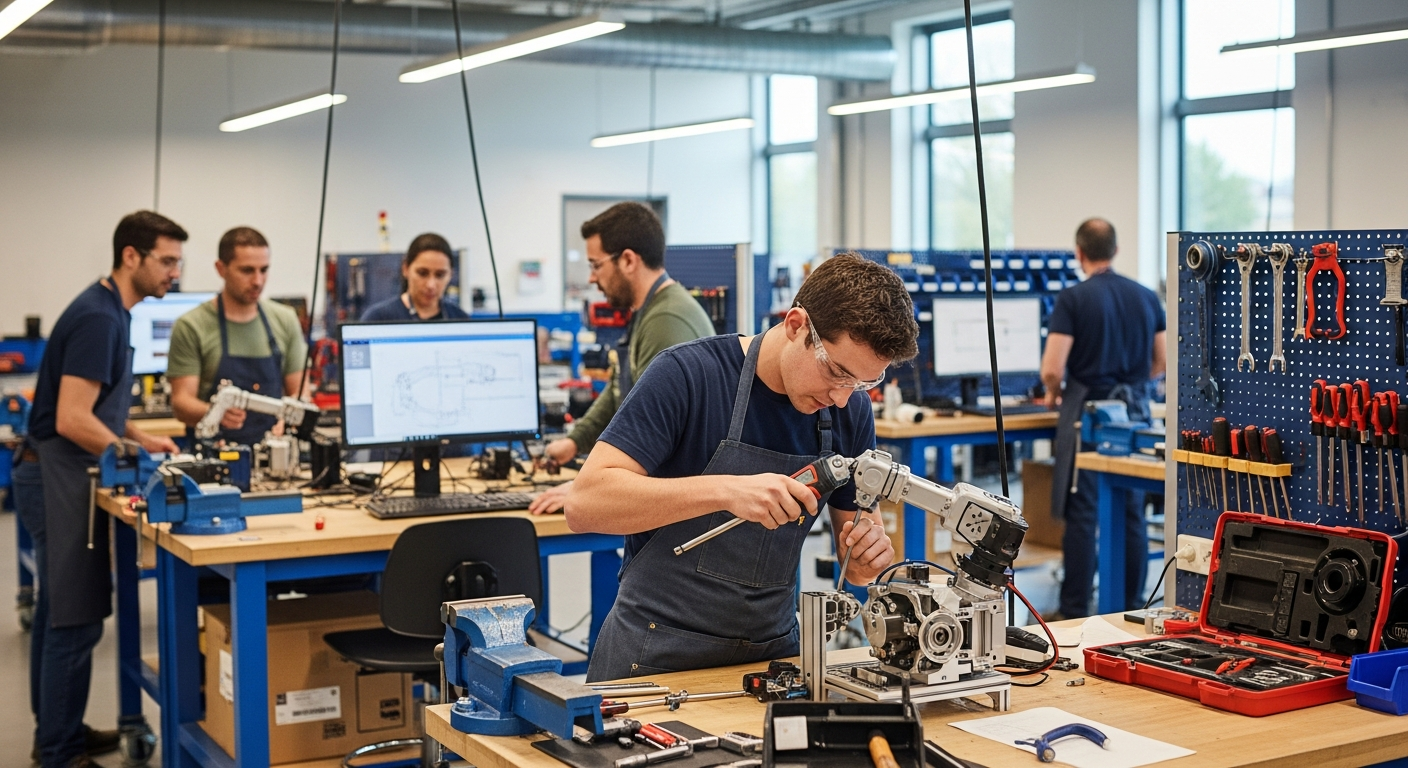
Agricultural machinery training in Germany is often described as a mix of technical foundations and supervised practice with modern farm equipment. Programs are usually organized into modules or learning blocks that progress from basic principles to more complex systems. Participants may start with an introduction to agricultural technology, then move through mechanical, hydraulic, and electrical systems before advancing to diagnostics and troubleshooting. The structure varies by provider, but most programs aim to balance theoretical knowledge with practical application, ensuring learners can apply what they study in real-world settings.
What Learning Blocks Are Commonly Covered
Common learning blocks often include mechanics, hydraulics, basic electrics, and diagnostics alongside workshop routines. Mechanics modules typically cover engine operation, transmission systems, and the maintenance of moving parts. Hydraulics instruction focuses on fluid power systems that control implements and machinery functions. Basic electrical training introduces participants to wiring, sensors, and control systems found in modern equipment. Diagnostics teaches learners how to identify faults, interpret error codes, and perform systematic troubleshooting. Workshop routines emphasize proper tool use, maintenance schedules, and documentation practices that are essential in professional settings.
Why Are Safety Standards Central To The Training
Safety standards and operating procedures are usually presented as core parts of working with machinery. Agricultural equipment can pose significant risks if not handled correctly, so training programs place strong emphasis on protective measures, emergency protocols, and compliance with German workplace safety regulations. Participants learn to conduct pre-operation inspections, recognize hazards, use personal protective equipment, and follow lockout-tagout procedures during maintenance. Understanding these standards is not only a legal requirement but also a practical necessity for anyone working in the field.
What Training Environments Are Used
Training environments may combine classroom, lab, and hands-on sessions depending on the provider. Classroom instruction typically covers theoretical concepts, technical drawings, and system diagrams. Laboratory sessions allow learners to examine components, conduct measurements, and practice assembly and disassembly in a controlled setting. Hands-on sessions take place in workshops or on training farms where participants operate actual machinery under supervision. Some providers also incorporate simulator technology to replicate equipment operation without the risks associated with live machinery. The mix of environments helps reinforce learning and build confidence before participants work independently.
How Can You Compare Different Training Options
Comparing options may involve duration, prerequisites, assessments, and the types of equipment used without promising specific outcomes. Program lengths can range from short intensive courses lasting a few weeks to comprehensive programs spanning several months. Prerequisites vary, with some courses open to beginners and others requiring prior technical knowledge or vocational qualifications. Assessment methods might include written exams, practical tests, or portfolio submissions. The types of equipment featured in training also differ, with some programs focusing on tractors and tillage equipment, while others include harvesters, sprayers, or precision farming technology. Prospective participants should consider their current skill level, career goals, and the specific machinery they wish to work with when evaluating programs.
| Training Provider Type | Typical Duration | Equipment Focus | Assessment Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vocational Schools | 6-12 months | Tractors, Implements | Written & Practical Exams |
| Private Training Centers | 4-8 weeks | Modern Farm Equipment | Skills Demonstrations |
| Manufacturer Workshops | 1-4 weeks | Brand-Specific Machinery | Certification Tests |
| Agricultural Colleges | 1-2 years | Comprehensive Range | Exams & Projects |
What Should You Consider Before Enrolling
Before enrolling in agricultural machinery training, it is important to clarify your objectives and research the credentials of the training provider. Consider whether you need a recognized qualification for employment or if you are seeking to update specific skills. Check if the program is accredited by relevant agricultural or technical bodies in Germany. Review the curriculum to ensure it covers the systems and equipment relevant to your interests. Ask about instructor qualifications, class sizes, and the availability of equipment for practical sessions. Some programs may offer flexible scheduling or modular formats that allow you to complete training while working. Taking time to gather this information will help you select a program that aligns with your needs and provides genuine value.
Agricultural machinery training in Germany reflects the country’s strong tradition of technical education and its commitment to maintaining high standards in the agricultural sector. Whether you are entering the field for the first time or looking to expand your expertise, understanding the typical structure and content of these programs can guide you toward a choice that supports your professional development and career aspirations.