Crucial Skills for the UK's Resource Management Industry
The resource management industry in the United Kingdom is often described as a sector that relies on a specific mix of technical, operational, and organizational skills. This article provides an informative overview of the key skills commonly associated with work in the UK’s resource and waste management industry, explaining how these competencies are applied across different roles and work environments. It explores practical abilities, safety awareness, and coordination skills that are frequently highlighted when discussing this field, as well as how these skills support day-to-day operations. The content is purely informational and is intended to help readers better understand which skills are considered important in the resource management industry, without presenting job offers, guarantees, or specific career outcomes.
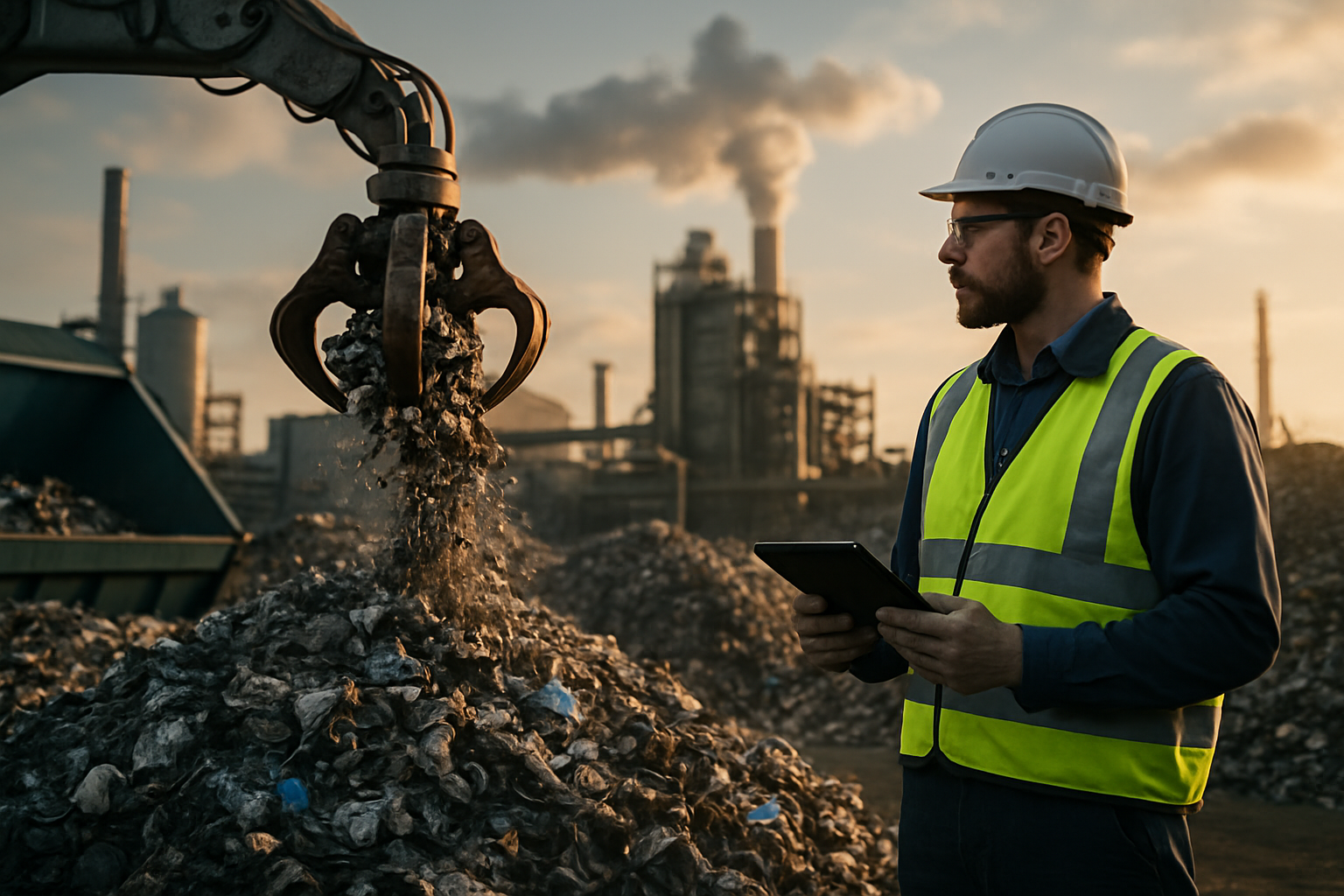

The resource management sector encompasses a wide range of activities, from collection and sorting to processing and disposal of materials. Professionals working in this field must possess a combination of technical knowledge, operational expertise, and interpersonal skills to navigate the complexities of modern waste and resource management systems.
Overview of key skills commonly associated with the resource management industry in the United Kingdom
The foundation of success in resource management rests on several core competencies. Environmental awareness stands as a fundamental requirement, as workers must understand the impact of waste on ecosystems and communities. Regulatory knowledge is equally important, given the extensive framework of UK and EU-derived environmental legislation governing waste handling, transportation, and disposal. Communication skills enable effective collaboration with colleagues, clients, and regulatory bodies, while problem-solving abilities help address the unexpected challenges that arise in daily operations. Digital literacy has become increasingly relevant as the industry adopts sophisticated tracking systems, route optimization software, and data management platforms.
Description of technical and operational abilities applied in waste and resource management roles
Technical competence forms the backbone of practical work in resource management. Equipment operation skills are essential, as many roles involve handling specialized machinery such as compactors, balers, forklifts, and collection vehicles. Understanding material properties helps workers identify recyclable materials, hazardous substances, and contamination issues that could compromise processing streams. Process knowledge enables efficient sorting, separation, and treatment of various waste types according to established protocols. Maintenance awareness ensures that equipment remains in safe working order, reducing downtime and preventing accidents. Quality control skills help maintain standards throughout collection, processing, and disposal operations, ensuring compliance with industry benchmarks and customer expectations.
Explanation of safety awareness and procedural knowledge used in daily operations
Safety consciousness permeates every aspect of resource management work. Workers must recognize potential hazards associated with handling unknown materials, operating heavy machinery, and working in varied weather conditions. Personal protective equipment knowledge ensures appropriate use of gloves, high-visibility clothing, safety footwear, and respiratory protection when necessary. Understanding emergency procedures prepares staff to respond effectively to incidents such as chemical spills, equipment malfunctions, or injuries. Risk assessment skills enable workers to evaluate situations before proceeding, identifying potential dangers and implementing control measures. Health and hygiene awareness protects both workers and the public from exposure to harmful substances and biological hazards commonly encountered in waste streams.
Outline of organizational and coordination skills relevant to resource management work
Effective resource management requires strong organizational capabilities. Time management skills help workers complete collection routes, processing tasks, and administrative duties within scheduled timeframes. Route planning abilities optimize collection efficiency, reducing fuel consumption and vehicle wear while ensuring timely service delivery. Record-keeping competence supports accurate documentation of waste quantities, types, and destinations, which is essential for regulatory compliance and operational analysis. Customer service skills facilitate positive interactions with residential and commercial clients, addressing concerns and providing guidance on proper waste separation. Team coordination enables smooth collaboration among drivers, loaders, sorters, and supervisors, ensuring that operations flow smoothly across shifts and locations.
Contextual view of how these skills support different work environments within the industry
The application of these competencies varies across the diverse settings found within resource management. Collection operations demand physical stamina, weather resilience, and public interaction skills as workers navigate residential streets and commercial premises. Processing facilities require technical expertise in operating sorting equipment, identifying material grades, and maintaining quality standards in high-volume environments. Transfer stations call for coordination abilities to manage incoming waste streams and outgoing processed materials efficiently. Recycling centers benefit from customer service skills as staff assist the public with material drop-off and provide guidance on acceptable items. Administrative roles within resource management companies rely heavily on digital skills, regulatory knowledge, and communication abilities to support field operations and maintain compliance. Supervisory positions require leadership capabilities, strategic thinking, and the ability to balance operational demands with safety requirements and environmental responsibilities.
The resource management industry continues to develop in response to environmental challenges, technological innovation, and changing public attitudes toward waste. The skills outlined above provide a framework for understanding the competencies that enable this essential sector to function effectively. As the United Kingdom pursues ambitious recycling targets and circular economy initiatives, the importance of a skilled workforce capable of adapting to new methods and technologies becomes increasingly apparent. Individuals considering involvement in this field can use this knowledge to assess their existing abilities and identify areas for development, while organizations can recognize the diverse skill sets that contribute to successful operations across all levels of the industry.