Mechanical Engineering Training in Sheffield – Build a Strong Technical Foundation
Mechanical engineering training in Sheffield is often described as a structured way to gain a clear understanding of how technical foundations are built for modern engineering fields. This article provides an informative overview of how training programs in mechanical engineering are typically organized in the Sheffield area, which core subjects and practical elements are commonly included, and how learning paths focus on developing fundamental technical knowledge. The content explains what learners can usually expect from such programs without suggesting guaranteed results, job placement, or specific career outcomes. It is intended to help readers understand how mechanical engineering training contributes to building a strong technical foundation in a realistic and balanced way
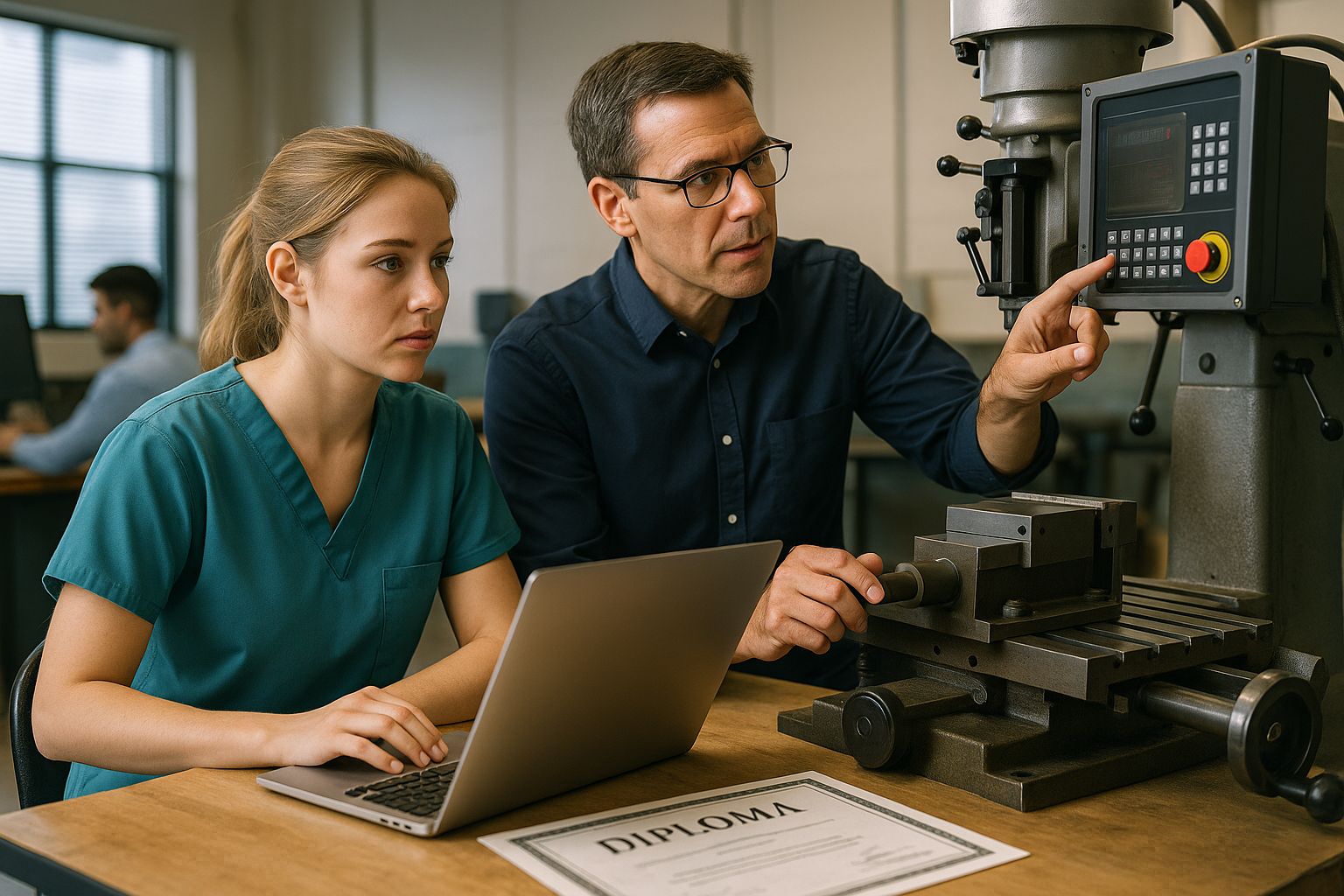

Mechanical engineering training programs provide a structured pathway for developing technical expertise in one of the most versatile engineering disciplines. Sheffield, with its strong industrial heritage and educational institutions, offers various training opportunities that combine academic rigor with practical application.
Overview of How Mechanical Engineering Training Programs in Sheffield Are Typically Organized
Mechanical engineering training programs in Sheffield follow a structured approach that balances theoretical knowledge with practical skills development. Most programs begin with fundamental engineering principles before progressing to specialized areas. Training is typically organized into modules or units, each focusing on specific aspects of mechanical engineering. The progression usually starts with basic mathematics and physics concepts, then advances to engineering-specific subjects like mechanics, thermodynamics, and materials science.
Programs often span multiple years, with each academic year building upon previous knowledge. Full-time courses typically run over three to four years, while part-time and evening programs may extend over longer periods to accommodate working professionals. The structure allows for gradual skill development, ensuring learners can absorb complex concepts before moving to advanced topics.
Core Subjects and Practical Elements Commonly Included in Mechanical Engineering Training
Mechanical engineering training encompasses a broad range of subjects essential for technical competency. Core theoretical subjects typically include mathematics, physics, thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, materials science, and engineering design. These foundational areas provide the scientific basis for understanding mechanical systems and processes.
Practical elements form a crucial component of training programs. Laboratory sessions allow students to conduct experiments, test theories, and observe real-world applications of engineering principles. Workshop sessions provide hands-on experience with manufacturing processes, machining, and assembly techniques. Computer-aided design (CAD) training teaches students to create technical drawings and 3D models, while simulation software helps them analyze and optimize designs.
Many programs also include project work, where students apply their knowledge to solve real engineering problems. These projects often involve designing, building, and testing mechanical systems or components, providing valuable experience in the complete engineering process.
How Learning Paths Focus on Building Fundamental Technical Knowledge
Learning paths in mechanical engineering training are carefully designed to build technical knowledge systematically. The approach typically follows a pyramid structure, with broad foundational subjects at the base and specialized topics at higher levels. Mathematics and physics form the foundation, providing the analytical tools needed for engineering calculations and problem-solving.
As students progress, they encounter increasingly complex engineering concepts. Statics and dynamics introduce the principles of force and motion, while thermodynamics explores energy transfer and conversion. Materials science teaches students about the properties and behavior of different materials under various conditions. Machine design courses combine multiple disciplines to teach students how to create functional mechanical systems.
The learning path also emphasizes the development of analytical thinking and problem-solving skills. Students learn to break down complex problems into manageable components, apply appropriate engineering principles, and develop practical solutions. This systematic approach ensures that graduates possess both the theoretical knowledge and practical skills needed in professional engineering environments.
What Learners Can Generally Expect From Mechanical Engineering Training Without Guaranteed Outcomes
Learners entering mechanical engineering training can expect a challenging but rewarding educational experience. The workload is typically substantial, requiring dedication to both theoretical study and practical work. Students should be prepared for intensive mathematical and scientific content, particularly in the early stages of training.
The learning environment often includes lectures, tutorials, laboratory sessions, and project work. Students can expect to work both independently and in teams, developing communication and collaboration skills alongside technical expertise. Assessment methods typically include written examinations, coursework assignments, laboratory reports, and project presentations.
While training programs aim to prepare students for engineering careers, outcomes depend on individual effort, aptitude, and market conditions. Successful completion of training typically provides the knowledge and skills foundation needed for entry-level engineering positions, but career progression depends on continued learning and professional development.
Informational Explanation of How Training Supports a Strong Technical Foundation
Mechanical engineering training supports the development of a strong technical foundation through its comprehensive and systematic approach. The curriculum is designed to ensure students understand fundamental principles before tackling advanced concepts. This methodical progression helps build confidence and competence in technical problem-solving.
The integration of theoretical and practical learning reinforces understanding and helps students see the real-world applications of engineering principles. Laboratory work and projects provide opportunities to test theories, observe phenomena, and develop practical skills. This hands-on experience is crucial for developing engineering intuition and understanding the limitations and capabilities of different systems and materials.
Training programs also emphasize the development of analytical and critical thinking skills. Students learn to approach problems systematically, consider multiple solutions, and evaluate the merits of different approaches. These skills are transferable and valuable throughout an engineering career, enabling professionals to adapt to new technologies and challenges as they arise.
The strong technical foundation developed through mechanical engineering training provides a platform for lifelong learning and professional development. Graduates are equipped with the fundamental knowledge and skills needed to understand new technologies, adapt to changing industry requirements, and contribute effectively to engineering teams and projects.