"Riding the Wave of Hydrogen Fuel Cell Technology in the Automotive Industry"
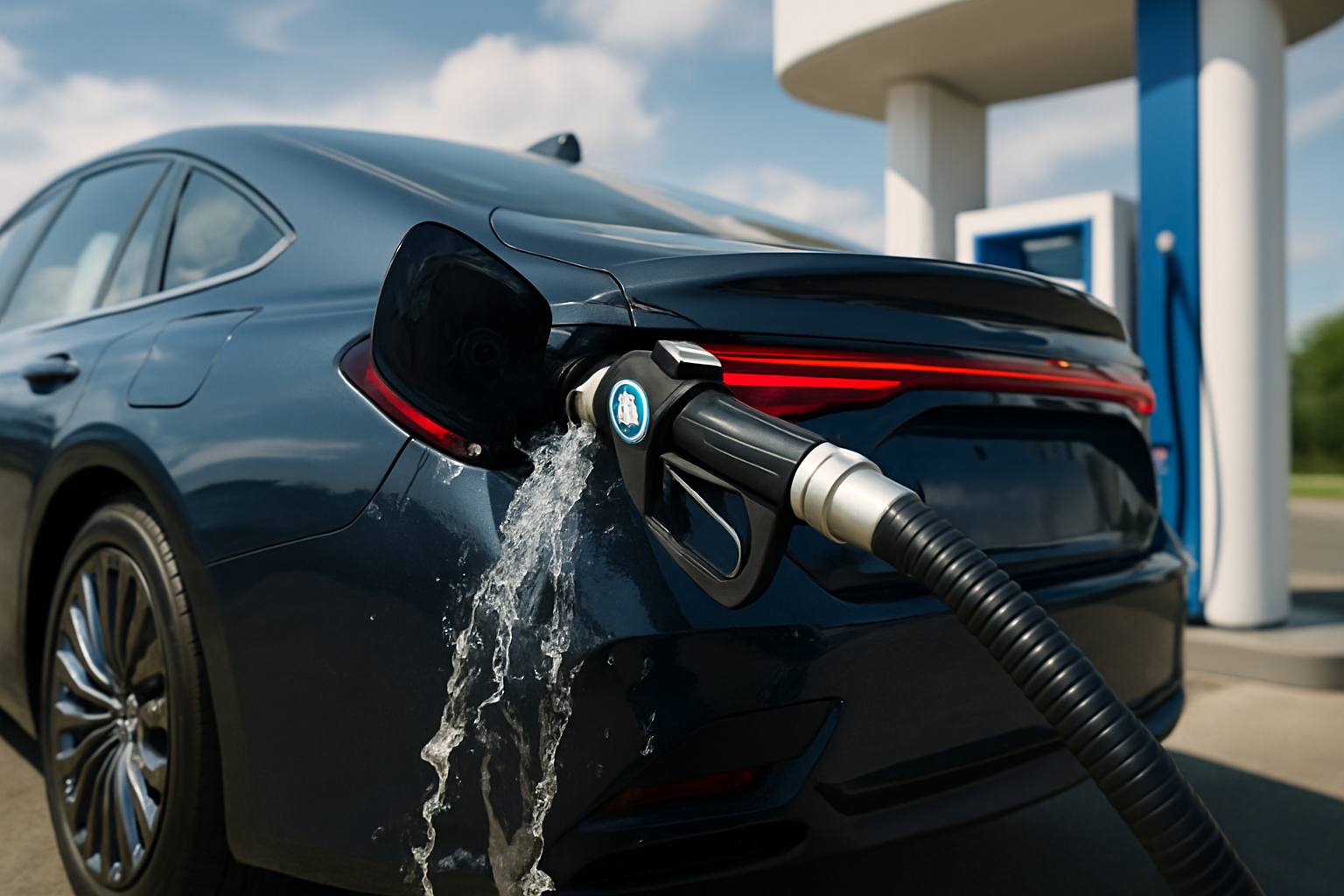
Imagine driving a car that only emits water as a byproduct. That's the promise of hydrogen fuel cell technology, a form of clean energy that could revolutionize the automotive industry. In the 1960s, during the height of the space race, NASA employed hydrogen fuel cells to generate power in spacecraft. The technology has since trickled down to the automotive industry, where it gained traction in the early 2000s. Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) operate by combining hydrogen stored in a tank with oxygen from the air to produce electricity, which powers an electric motor. The only byproduct of this process is water vapor.

Current Trends in Hydrogen Fuel Cell Technology
FCVs are not as prevalent as traditional gas-powered cars or electric vehicles (EVs), but they are gaining momentum. Major automakers like Toyota, Hyundai, and Honda have invested heavily in this technology, with Toyota’s Mirai and Hyundai’s Nexo leading the pack. These companies believe that the long-range and quick refueling capabilities of FCVs can make them a viable alternative to EVs, especially for commercial use.
The Pros and Cons of Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles
Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles have several advantages over traditional cars and EVs. They have longer driving ranges, typically exceeding 300 miles on a full tank of hydrogen, and can be refueled in just a few minutes, similar to a traditional gas-powered car. Hydrogen is abundant and can be produced from various renewable sources, making it a sustainable fuel option.
However, FCVs also face significant challenges. The most notable is the lack of infrastructure. Hydrogen refueling stations are scarce, making long-distance travel in FCVs tricky. Furthermore, the process of producing, transporting, and storing hydrogen is energy-intensive and can contribute to greenhouse gas emissions if not managed correctly.
The Future of Hydrogen Fuel Cell Technology
Despite these challenges, the future of hydrogen fuel cell technology in the automotive industry is promising. Governments and automakers around the world are investing in the development of hydrogen infrastructure. In Europe, for example, the Hydrogen Mobility Europe project aims to deploy 49 hydrogen refueling stations and 1,400 fuel cell vehicles by 2022.
The potential environmental benefits of FCVs are also driving interest. As nations strive to reduce carbon emissions, hydrogen fuel cell technology could play a key role in creating a greener automotive industry.
Conclusion
Hydrogen fuel cell technology has the potential to transform the automotive industry, offering a clean, sustainable form of energy that could reduce our reliance on fossil fuels. Despite the challenges, the push towards a hydrogen economy is gaining momentum, and it will be fascinating to watch how this technology evolves in the coming years.